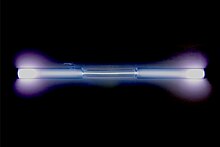
Xenon, 54 A xenon-filled
discharge tube glowing light blue
Pangucapan Wujud Colorless gas, exhibiting a blue glow when placed in a high voltage electric field Bobot atom standar (A r, standard ) 7002131293000000000♠ 131.293(6)[ 3]
Atomic number (Z ) 54 Group group 18 (noble gases) Period period 5 Blok p-block Konfigurasi èlèktron [Kr ] 5s2 4d10 5p6 Electrons per shell
2, 8, 18, 18, 8 Phase at STP gas Melting point 161.4 K (-111.7 °C, -169.1 °F) Boiling point 165.03 K (-108.12 °C, -162.62 °F) Density (at STP) 5.894 g/L when liquid (at b.p. ) 3.057[ 4] 3 Triple point 161.405 K, 81.6[ 5] Critical point 289.77 K, 5.841 MPa Heat of fusion 2.27 kJ/mol Heat of vaporization 12.64 kJ/mol Molar heat capacity 5R /2 = 20.786 J/(mol·K) Vapor pressure
P (Pa)
1
10
100
1 k
10 k
100 k
at T (K)
83
92
103
117
137
165
Oxidation states 0 , +1, +2, +4, +6, +8 acidic oxideElectronegativity Pauling scale: 2.6 Covalent radius 140±9 pm Van der Waals radius 216 pm Crystal structure face-centered cubic (fcc) Speed of sound (liquid) 1090 m/s ; (gas) 169 m/s Thermal conductivity 5.65×10-3 W/(m·K) Magnetic ordering diamagnetic [ 6] CAS Number 7440-63-3
| references | in Wikidata
Réferènsi Daftar réferènsi bakal muncul jroning artikel utama.
↑ Simpson, J. A.; Weiner, E. S. C., èd. (1989). "Xenon". Oxford English Dictionary Clarendon Press . ISBN 0-19-861232-X ↑ "Xenon" . Dictionary.com Unabridged . 2010. Dibukak ing 2010-05-06 .↑ Meija, J.; et al. (2016). "Atomic weights of the elements 2013 (IUPAC Technical Report)" . Pure and Applied Chemistry 88 (3): 265–91. doi :10.1515/pac-2015-0305 . ↑ "Krypton" . Gas Encyclopedia . Air Liquide. 2009.↑ Lide, David R. (2004). "Section 4, Properties of the Elements and Inorganic Compounds; Melting, boiling, triple, and critical temperatures of the elements". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (édhisi ka-85). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 0849304857 ↑ Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds , in Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 81st edition, CRC press. ↑ J. A. Simpson & E. S. C. Weiner, èd. (1989). "Xenon". Oxford English Dictionary ISBN 0-19-861232-X ↑ "Xenon" . Dictionary.com Unabridged . 2010. Dibukak ing 2010-05-06 .